About Electrocardiograms (EKG/ECG)
Learn More About Electrocardiograms (EKG/ECG):
Electrocardiograms (ECG or EKG)
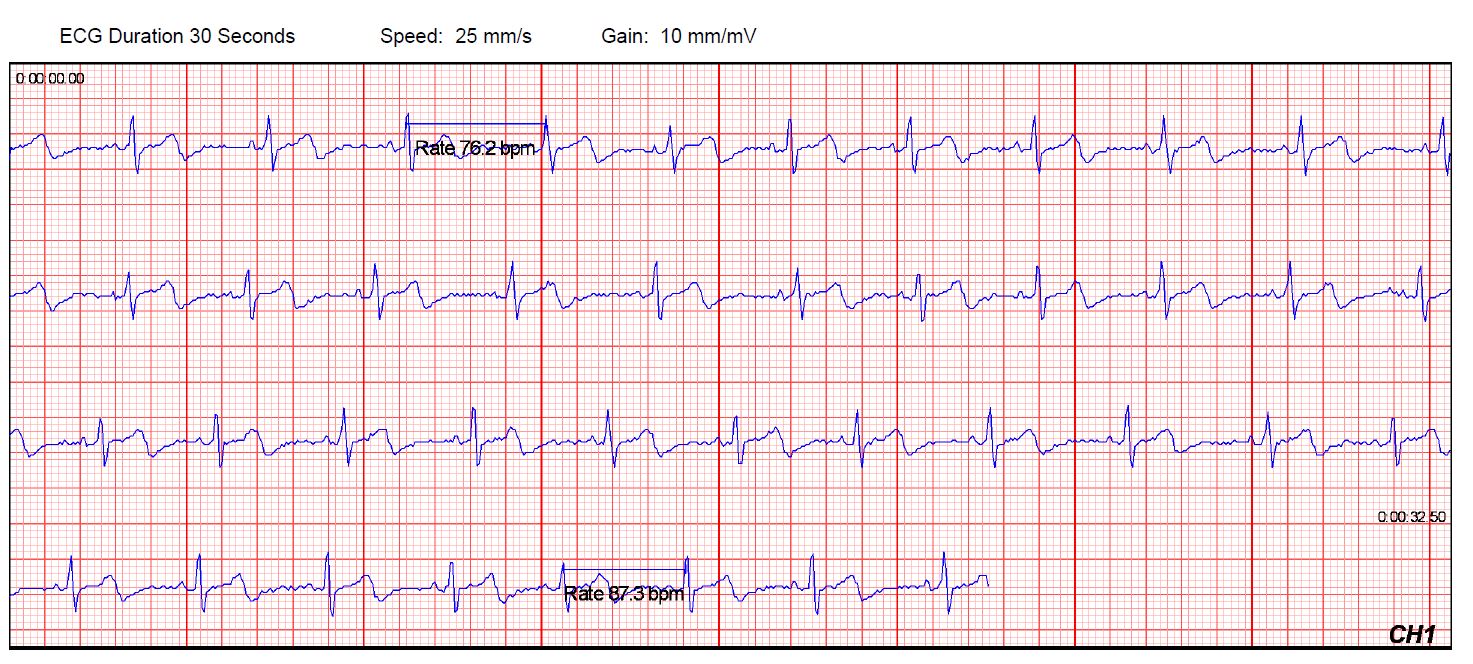
EKG Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Want to learn more about EKGs?
Visit our dedicated FAQ section on the topic.
- EKG
- GEMS™ Win
This website offers general ECG information for educational purposes only. We are not licensed medical professionals. Content should not be construed as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. For personalized guidance, consult a qualified healthcare provider.
Principles of ECG
The ECG works based on the principles of electrical conduction in the heart. The heart generates electrical impulses that trigger each heartbeat. These impulses spread through the heart in a specific sequence, resulting in muscle contractions. The ECG records these electrical impulses as waveforms. The primary components of an ECG waveform are:
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization, which is the electrical impulse that causes the atria to contract.
- QRS Complex: Reflects ventricular depolarization, signaling the contraction of the ventricles. It is typically the largest and most prominent part of the ECG.
- T Wave: Represents ventricular repolarization, indicating the recovery phase of the ventricles.
- ST Segment: This segment shows the interval between ventricular depolarization and repolarization and is used to assess myocardial ischemia or injury.
- QT Interval: Reflects the time taken for both ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
- RR Interval: Represents the time between two consecutive heartbeats, which is used to determine heart rate.
More about EKG/ECG…
ECG Leads
Electrocardiography uses multiple leads to record electrical activity from various angles. The leads can be categorized into three main groups:
- Standard Limb Leads (I, II, III): These leads measure electrical activity between the limbs and provide a frontal plane view of the heart’s electrical activity.
- Augmented Limb Leads (aVR, aVL, aVF): These leads are calculated using a combination of the limb leads to view the heart’s electrical activity from different angles.
- Precordial (Chest) Leads (V1-V6): These leads are positioned on the chest and provide a transverse or horizontal plane view of the heart’s electrical activity. They are particularly useful for detecting changes in the anterior, lateral, and inferior walls of the heart.
Clinical Applications of ECG
ECG is an invaluable tool in clinical medicine, and it is used for a wide range of purposes, including:
- Diagnosing Arrhythmias: ECG can identify various types of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and bradycardia.
- Evaluating Myocardial Infarction: ECG can detect signs of myocardial infarction (heart attack) by assessing ST-segment elevations or depressions.
- Monitoring Heart Health: ECGs are used to monitor patients with known heart conditions, such as congestive heart failure or long QT syndrome.
- Assessing Cardiac Structure: ECG can help identify conditions like left ventricular hypertrophy and atrial enlargement.
- Preoperative Assessment: It is essential in the evaluation of patients before surgery to determine their cardiac risk.
- Screening: ECG is employed in sports medicine to screen athletes for underlying heart conditions that may lead to sudden cardiac events during physical activity.
ECG Technology Advancements
The field of ECG has seen significant technological advancements in recent years.
- Digital ECG: Modern ECG machines use digital technology to produce high-quality recordings that can be stored electronically, making them easily accessible for review and analysis.
- Telemedicine: ECGs can now be performed remotely, with the results transmitted to healthcare providers for real-time assessment, allowing for quicker diagnosis and intervention.
- Machine Learning and AI: Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being used to assist in the interpretation of ECG data, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Wearable ECG Devices: Consumer-oriented wearable devices can record ECG data continuously, allowing individuals to monitor their heart health and share data with healthcare professionals.

